Branching (b*)
Branching commands in Hug simplify managing local and remote branches. Prefixed with b for "branch", they provide intuitive ways to list, switch, create, delete, and query branches with safety checks and clear output.
These commands are implemented as Git aliases and scripts in the Hug tool suite, wrapping Git's branch operations for better usability, including interactive selection, color highlighting, and formatted views.
Quick Reference
| Command | Memory Hook | Summary |
|---|---|---|
hug b | Branch checkout | Switch to an existing branch or pick interactively |
hug br | Branch Remotes | Alias for hug b -r: Interactive menu of remote branches only; create tracking on select |
hug brr | Branch Refreshed Remotes | Alias for hug b -R: As above, but fetch/prune remotes first |
hug bl | Branch List | List local branches |
hug bla | Branch List All | List local and remote branches |
hug blr | Branch List Remote | List remote branches only |
hug bll | Branch List Long | Detailed local branch list with tracking info |
hug bcp <source> [dest] | Branch CP (copy) | Create a copy of a branch or commitish without switching; auto-names if unspecified |
hug bc | Branch Create | Create a new branch and switch to it |
hug bc --no-switch | Branch Create no-switch | Create a new branch without switching to it |
hug bmv | Branch MV (move) | Rename the current branch |
hug brestore | Branch RESTORE | Restore a branch from a backup |
hug bdel | Branch DELete | Delete branches interactively or by name |
hug bdel-backup | Branch DELete BACKUP | Delete backup branches with filters |
hug bdelf | Branch DELete Force | Force-delete local branch |
hug bdelr | Branch DELete Remote | Delete remote branch |
hug bpull | Branch Pull | Safe fast-forward pull (fails if merge/rebase needed) |
hug bpullr | Branch Pull Rebase | Pull with rebase (linear history) |
hug bwc | Branch Which Contain | Branches containing a commit |
hug bwp | Branch Which Point | Branches pointing at an object |
hug bwnc | Branch Which Not Contain | Branches missing a commit |
hug bwm | Branch Which Merged | Branches merged into a commit |
hug bwnm | Branch Which Not Merged | Branches not merged into a commit |
Listing Branches
hug b [branch]
Description: Switch (checkout) to an existing local branch. If no branch is specified, shows an interactive menu of local branches for selection. If the specified branch doesn't exist locally,
hug bautomatically searches for a matching remote branch (e.g.,origin/branch-name) and creates a local tracking branch. If no match is found anywhere, it errors out safely.Options:
-r, --remote: Display an interactive menu of only remote branches. Selecting one creates and switches to a local tracking branch. Use this when you want to discover and pull in remote work without listing locals first. Requires no branch argument.-R, --refresh: Like--remote, but first fetches branch data from the remote to ensure up-to-date information. Ideal before switching in shared repos; if fetch fails (e.g., network issues), it warns and uses cached data.
Aliases:
hug br: Equivalent tohug b -r(remote branches menu).hug brr: Equivalent tohug b -R(refreshed remote branches menu).
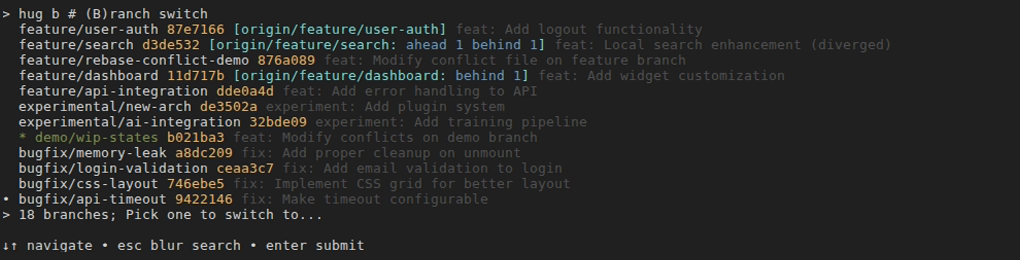
Interactive Selection Behavior: The menu lists branches as: branch-name (short-hash) [upstream info, e.g., ahead/behind counts], followed by the commit subject line. The current branch is highlighted in green with an asterisk (*). By default, shows local branches. With
-ror-R, shows remotes only (with remote prefix in cyan brackets, e.g., [origin/main]). For repos with 10+ branches, leveragesgum filter(install via charmbracelet/gum) for searchable, multi-select filtering. Otherwise, falls back to a simple numbered list for quick picks.Interactive Selection Behavior: The menu lists branches as: branch-name (short-hash) [upstream info, e.g., ahead/behind counts], followed by the commit subject line. The current branch is highlighted in green with an asterisk (*). By default, shows local branches. With
-ror-R, shows remotes only (with remote prefix in cyan brackets, e.g., [origin/main]). For repos with 10+ branches, leveragesgum filter(install via charmbracelet/gum) for searchable, multi-select filtering. Otherwise, falls back to a simple numbered list for quick picks.Example:
shellhug b main # Switch to local 'main' (or create tracking from remote if missing) hug b feature/new-ui # Switch to local; if absent, auto-create from origin/feature/new-ui hug b origin/hotfix # Explicitly create local 'hotfix' tracking origin/hotfix hug b # Interactive local menu (searchable with gum if many branches) hug b -r # Interactive remote-only menu; select to create/switch local tracking hug b -R # As above, but fetches fresh remotes firstExamples assume a standard
originremote; works with other remotes via Git config.Safety: Interactive mode prevents accidental switches. Always checks if you're in a Git repo. Prevents stale switches by optionally refreshing remotes (
-R). Interactive mode avoids direct errors—e.g., no branches? Exits with a clear message. Fetch warnings ensure you're aware of potential outdated data.Use Cases:
- Quick remote onboarding:
hug b -rto browse and switch to a teammate's feature branch. - Safe experimentation: Use
-Rbefore switching in a team repo to avoid missing upstream changes. - Debugging history: Switch to a remote tag-like branch without manual setup.
- Quick remote onboarding:
After typing
perform: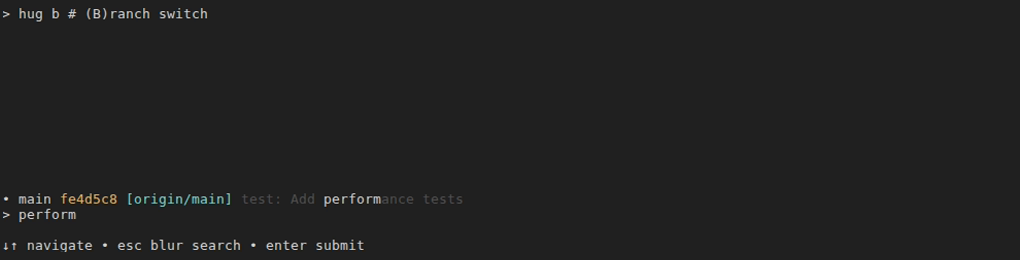
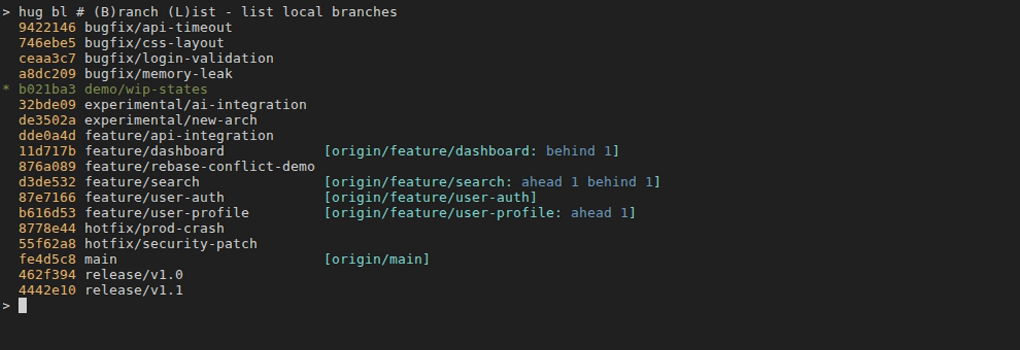
hug bl [term]
- Description: List local branches in short format, sorted alphabetically. The current branch is marked with an asterisk (*). Supports optional case-insensitive search filtering by branch name with multi-term OR logic.
- Examples:shell
hug bl # List all local branches hug bl feature # List branches containing "feature" hug bl feature auth # List branches with "feature" OR "auth" hug bl bug fix # List branches with "bug" OR "fix" - Safety: Read-only operation; no changes to repo state.
hug bla
- Description: List all branches (local and remote) in short format.
- Example:shell
hug bla # List all branches including remotes - Safety: Read-only.
hug blr
- Description: List remote branches only in short format.
- Example:shell
hug blr # List remote branches - Safety: Read-only.

hug bll [term]
- Description: List local branches in long format with details: short commit hash, upstream tracking info (e.g., ahead/behind counts), and the latest commit message title. Current branch is highlighted in green and marked with *. Branches are left-aligned for readability. Supports optional case-insensitive search filtering by branch name with multi-term OR logic.
- Examples:shell
hug bll # Detailed local branch listing hug bll fix # List branches containing "fix" hug bll fix bug # List branches with "fix" OR "bug" hug bll feature auth # List branches with "feature" OR "auth" - Safety: Read-only; displays tracking info like
git branch -vvbut with commit subjects. 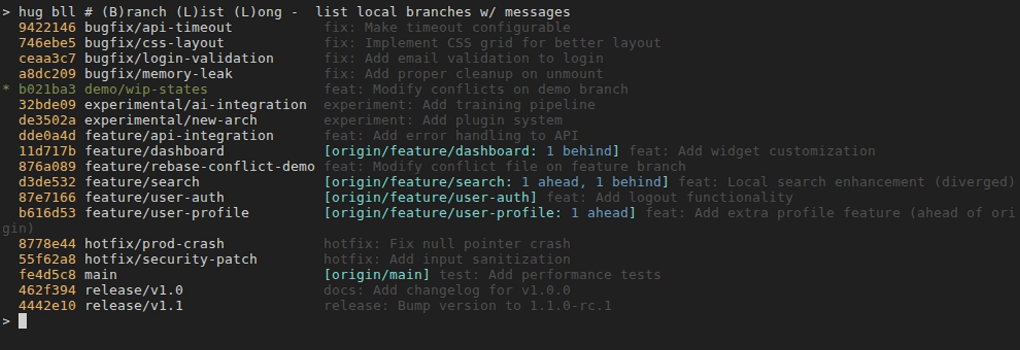
Branch Creation / Modification
hug bc [<branch-name>] [--point-to <commitish>] [--no-switch]
- Description: Create a new branch and switch to it. By default, creates from current HEAD. With
--point-to, you can create a branch from any commit, tag, or branch. Use--no-switchto create without switching (stay on current branch). - Arguments:
<branch-name>- Name for the new branch (optional with--point-to)--point-to <commitish>- Create branch pointing to a specific commit, tag, or branch--no-switch- Create without switching to the new branch
- Auto-Generated Names: When using
--point-towithout a branch name, automatically generates a descriptive name:- If target is a branch:
<branch>.copy.<iso-datetime> - If target is not a branch:
<target>.branch.<iso-datetime> - ISO datetime format: YYYYMMDD-HHMM (e.g., 20251109-1430)
- If target is a branch:
- Aliases and Variants:
hug bcp <source> [dest]is a convenient alias forhug bc --no-switch --point-to <source> [dest], ideal for creating branch snapshots (e.g., Branch CP for copy). It leverages the same auto-naming but keeps you on the current branch to avoid workflow interruption. Preferbcpfor quick copies; use fullbcflags for advanced control. Cross-referenceshug ccpfor commit-level copies.
- Examples:shell
hug bc new-feature # Create branch from current HEAD hug bc --point-to abc123 my-feature # Create branch from commit abc123 hug bc --point-to v1.0.0 # Auto-generate name from tag v1.0.0 hug bc --point-to main # Auto-generate name: main.copy.20251109-1430 hug bc my-feature --point-to abc123 # Flag can come after branch name hug bc --no-switch snapshot-branch # Create without switching hug bc --no-switch --point-to v1.0.0 # Auto-generate and create without switching # bcp-specific examples hug bcp origin/release/v1.0 hotfix-v1.0 # Copy remote branch explicitly hug bcp HEAD~3 debug-branch # Copy from 3 commits back hug bcp main # Auto-generate: main.copy.20251109-1430 (no switch) - Use Cases:
- From a tag: Quickly create a branch to investigate or patch a specific release
- From a commit: Create a branch from a specific point in history for debugging or feature development
- From another branch: Create a snapshot copy of a branch's current state
- Experimentation: Auto-generated names let you quickly create exploratory branches without thinking of names
- Backups/Snapshots: Use
--no-switchto create a branch reference without disrupting current work - Before rebasing a shared branch: Copy it with
hug bcp shared-main my-local-copyto preserve the original state
- Safety: Non-destructive; creates from specified point or current HEAD. Prompts if target name exists. For copies via
bcp, ensures uniqueness by appending seconds to timestamps if needed.
hug bmv <new-name>
- Description: Rename the current branch to a new name (alias for
git branch -m). - Example:shell
hug bmv updated-feature # Rename current branch - Safety: Prompts for confirmation if the new name exists.
hug brestore [<backup-branch>] [<target-branch>]
- Description: Restore a branch from a backup created by commands like
hug rb. Backups follow the naming conventionhug-backups/YYYY-MM/DD-HHMM.original-name. If no arguments are provided, shows an interactive menu of available backups. When there are 10 or more backup branches and gum is installed, uses an interactive filter for easier selection. Otherwise, displays a numbered list. If only the backup branch is specified, restores to the original branch name. If both arguments are provided, restores to a different branch name. - Examples:shell
hug brestore # Interactive: select from available backups (uses gum filter for 10+) hug brestore hug-backups/2025-11/02-1234.feature # Restore to 'feature' hug brestore hug-backups/2025-11/02-1234.feature recovered-feature # Restore to 'recovered-feature' hug brestore hug-backups/2025-11/02-1234.feature --dry-run # Preview restoration - Safety: Prompts for confirmation if the target branch already exists (destructive operation). Use
--dry-runto preview changes. The original backup branch is preserved after restoration.
Branch Deletion
hug bdel [<branch>...]
- Description: Interactively or directly delete one or more local branches. Supports multi-selection via
gum filterwhen no branches specified. - Examples:shell
hug bdel # Interactive: select branches with gum filter hug bdel old-feature # Delete single branch (merged only) hug bdel feat-1 feat-2 # Delete multiple branches hug bdel old-feat --force # Force delete unmerged branch hug bdel --dry-run # Preview what would be deleted - Features:
- Interactive multi-selection with
gum filter --no-limit(when no branches specified) - Excludes backup branches (use
hug bdel-backupfor those) - Shows confirmation with branch count before deletion
- Safe by default: only deletes merged branches (use
--forcefor unmerged)
- Interactive multi-selection with
- Safety: Requires confirmation unless
--forceis used; fails if trying to delete unmerged branches without--force.
hug bdel-backup [<backup>...] [--keep N] [--delete-older-than PATTERN]
- Description: Manage backup branches created by commands like
hug rb. Supports filtering by date and keeping N most recent backups. - Examples:shell
hug bdel-backup # Interactive: select backups to delete hug bdel-backup 2024-11/02-1234.feature # Delete specific backup (short form) hug bdel-backup --keep 5 # Keep 5 most recent, delete rest hug bdel-backup --delete-older-than 2024-11 # Delete backups from Nov 2024 and earlier hug bdel-backup --delete-older-than 2024-11/03 # Delete backups from Nov 3, 2024 and earlier hug bdel-backup --keep 3 --delete-older-than 2024 # Combine filters: delete 2024 and earlier, but keep 3 most recent overall - Filter Patterns:
YYYY- Year (e.g.,2024)YYYY-MM- Month (e.g.,2024-11)YYYY-MM/DD- Day (e.g.,2024-11/03)YYYY-MM/DD-HH- Hour (e.g.,2024-11/03-14)YYYY-MM/DD-HHMM- Minute (e.g.,2024-11/03-1415)
- Features:
- Interactive multi-selection with
gum filter --no-limit --keep N: Always preserve N most recent backups--delete-older-than: Delete backups with timestamps older than pattern- Combined filters:
--delete-older-thanidentifies candidates,--keepprotects most recent
- Interactive multi-selection with
- Safety: Always prompts for confirmation unless
--forceis used.
hug bdelf <branch>
- Description: Force-delete a local branch, even if unmerged. Direct alias to
git branch -D. - Example:shell
hug bdelf risky-branch # Force delete unmerged branch - Note: For safer multi-branch deletion with unmerged branches, use
hug bdel --forcewhich provides better UI and confirmation.
hug bdelr <branch>
- Description: Delete a remote branch from the
originremote. - Example:shell
# First, list remote branches to find the one to delete hug blr # Then, delete the desired branch by name hug bdelr old-remote-feature - Safety: Prompts for confirmation before deleting.
Pulling Branches
Hug provides safe, intuitive pull commands under the b* prefix, emphasizing fast-forward safety by default while offering rebase for linear histories.
hug bpull
- Description: Safe fast-forward pull from upstream. Succeeds only if your local branch can fast-forward (no local divergence); aborts otherwise to prevent unintended merges or rewrites. Ideal for verifying sync before critical operations like tagging or releasing.
- Example:shell
hug bpull # Pull if fast-forward possible; fails safely if diverged - Safety: Ultra-safe - aborts on any need for merge/rebase, prompting you to inspect with
hug slor usehug bpullr.
hug bpullr
- Description: Pull with rebase, replaying your local commits on top of remote changes for a clean, linear history. Use when you've diverged locally (e.g., after committing features).
- Example:shell
hug bpullr # Pull and rebase for linear history - Safety: Non-destructive to remote history, but may require conflict resolution. Aborts on issues; resume with
hug rbcor abort withhug rba. See the Rebase Conflict Workflow for a detailed guide on resolving conflicts.
Branch Queries (bw*)
These commands help inspect which branches relate to specific commits or states.
hug bwc [<commit>]
- Description: Show branches that contain a specific commit (in their history). Defaults to HEAD.
- Example:shell
hug bwc a1b2c3 # Branches containing commit a1b2c3 hug bwc # Branches containing HEAD - Safety: Read-only.

hug bwp [<object>]
- Description: Show branches that point exactly at a specific object (e.g., commit). Defaults to HEAD.
- Example:shell
hug bwp HEAD # Branches pointing at HEAD - Safety: Read-only.

hug bwnc [<commit>]
- Description: Show branches that do NOT contain a specific commit. Defaults to HEAD.
- Example:shell
hug bwnc HEAD # Branches not containing HEAD - Safety: Read-only.

hug bwm [<commit>]
- Description: Show branches merged into a specific commit (defaults to HEAD).
- Example:shell
hug bwm # Branches merged into HEAD - Safety: Read-only.

hug bwnm [<commit>]
- Description: Show branches NOT merged into a specific commit (defaults to HEAD).
- Example:shell
hug bwnm # Branches not merged into HEAD - Safety: Read-only.

Tips
- Use
hug bto review branch status and easily switch via an interactive menu. - Quick branch creation: Use
hug bc --point-to <target>without a branch name to quickly experiment - the auto-generated name includes a timestamp. - Branch from releases: Need to patch a production release? Use
hug bc --point-to v1.2.3to instantly create a branch from that tag. - Preserve branch state: Create a snapshot before risky operations:
hug bc --no-switch --point-to feature-branchcreates a timestamped copy without switching. - Use
hug blrto list remote branches before deleting one withhug bdelr. - Queries like
bwcandbwmare useful for cleanup beforebdel. - Commands like
hug rbautomatically create backup branches in thehug-backups/namespace. Usehug brestoreto restore them if needed. - Backup branches follow the naming convention
hug-backups/YYYY-MM/DD-HHMM.original-name, making them easy to identify and clean up. - Pair
hug b -Rwithhug sl(status) post-switch to verify sync. For detailed lists before interactive, usehug blr(remotes) orhug bll(locals with tracking).
See Status & Staging for checking changes after branching operations.