File Inspection (f*)
File inspection commands in Hug help you analyze the history and authorship of specific files. Prefixed with f for "file," they provide tools for blame (who changed what), contributor lists, author commit counts, and finding when a file was first added. These are especially useful for understanding code ownership and evolution over time.
When no file is provided, these commands will show an interactive file selection UI (requires gum to be installed). This makes it easy to explore files without memorizing paths.
Quick Reference
| Command | Memory Hook | Summary |
|---|---|---|
hug fblame | File Blame | Detailed blame with movement detection |
hug fb | File Blame (porcelain) | Lightweight blame output for scripting |
hug fcon | File CONtributors | List unique contributors to a file |
hug fa | File Authors | Count commits per author for a file |
hug fborn | File Born | Show the commit where the file was added |
Blame Commands
Blame shows which author last modified each line of a file, helping attribute changes.
hug fblame [<file>]- Description: Detailed blame showing author, date, and line content for each line in the file. Ignores whitespace changes and detects moved/copied code across files (up to 3 levels). When no file is provided, shows interactive file selection UI.
- Example:shell
hug fblame # Interactive file selection hug fblame src/app.js # Blame for app.js - Safety: Read-only; no repo changes.
- Git Equivalent:
git blame -w -C -C -C <file> 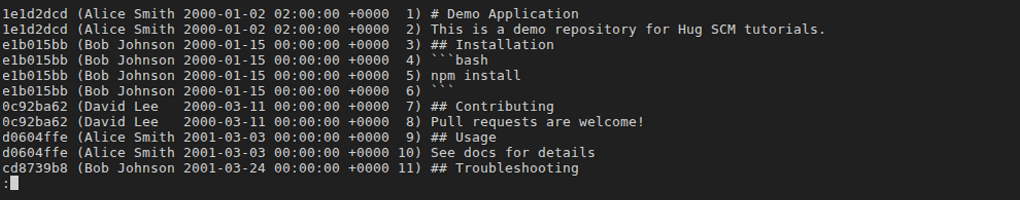
hug fb [<file>]- Description: Short blame output with just author and line number (porcelain format for scripting). When no file is provided, shows interactive file selection UI.
- Example:shell
hug fb # Interactive file selection hug fb README.md # Short blame for README.md - Safety: Read-only.
- Git Equivalent:
git blame -w -C -C -C --line-porcelain <file>
Contributor Analysis
hug fcon [<file>]- Description: List all unique contributors (authors with email) to a file, following renames. When no file is provided, shows interactive file selection UI.
- Example:shell
hug fcon # Interactive file selection hug fcon docs/index.md # Contributors to index.md - Safety: Read-only.
- Git Equivalent:
git log --follow --pretty=format:'%an <%ae>' -- <file> | sort -u 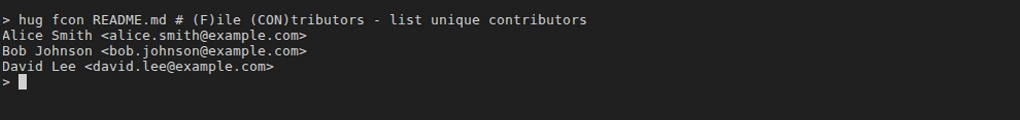
hug fa [<file>]- Description: Count commits per author for a file (sorted by count descending), following renames. When no file is provided, shows interactive file selection UI.
- Example:shell
hug fa # Interactive file selection hug fa lib/utils.js # Author commit counts for utils.js - Safety: Read-only.
- Git Equivalent:
git log --follow --format='%an' -- <file> | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn 
File Origin
hug fborn [<file>]- Description: Show the commit where the file was first added (born), including the full commit details and message. Handles renames with a 40% similarity threshold. When no file is provided, shows interactive file selection UI.
- Usage:shell
hug fborn # Interactive file selection hug fborn package.json # When package.json was added - Safety: Read-only.
- Git Equivalent:
git log --pretty=logbody --follow --diff-filter=A --find-renames=40% -- <file> 
Tips
- Combine with Logging for broader file history: e.g., use
hug llf <file> -1for the latest commit, thenhug fblame <file>to see line authors. - For detecting code movement across files,
fblameandfbuse advanced-C -C -Coptions - great for refactors. - Pipe outputs to tools:
hug fa <file> | head -5for top 5 contributors. - Always use
--followimplicitly for rename-aware inspection.
Pair with Status & Staging to inspect current file changes, or Logging for commit-level details.